Clean Energy
3 Learnings for Scaling Up Wind and Solar Power
The following content is sponsored by the National Public Utilities Council
3 Learnings for Wind and Solar Power Scale-Up
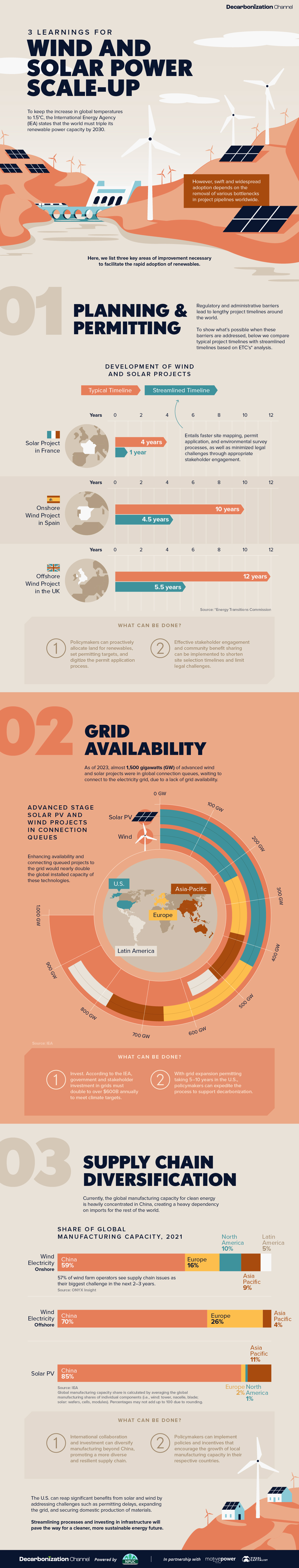
To keep the increase in global temperatures to 1.5°C, the International Energy Agency (IEA) states that the world must triple its renewable power capacity by 2030.
However, swift and widespread adoption depends on the removal of various bottlenecks in project pipelines worldwide.
We’ve partnered with the National Public Utilities Council to visualize data from the IEA and the Energy Transitions Commission to highlight three areas of improvement, critical to the rapid adoption of renewables.
1. Planning and Permitting
Currently, regulatory and administrative barriers lead to lengthy project timelines worldwide.
A wind project, for example, can take 10–12 years of development, while solar projects can take four years.
The Energy Transitions Commission suggests a faster process, including quicker site mapping, permit applications, and environmental surveys.
Policymakers can help reduce project timelines by allocating land for renewables, setting permit targets, and digitalizing the permit application process. As a result, the development time for wind projects could be reduced to 4.5–5.5 years, and solar projects could be online in one year.
2. Grid Availability for Solar and Wind
Connecting renewable energy projects to the grid has posed a challenge.
As of 2023, almost 1,500 gigawatts (GW) of wind and solar projects in advanced stages of development were still off the electricity grid.
Excluding China and India, transmission and distribution investments have increased by only 1% annually since 2010. According to the IEA, however, government and stakeholder investment in grids must double to over $600 billion annually to meet climate targets.
3. Supply Chain Diversification
The final area for improvement, when it comes to expediting global wind and solar power scale-up, is supply chain diversification.
Currently, China heavily concentrates the global manufacturing capacity on clean energy, leading to a heavy dependency on imports for the rest of the world.
| Share of Manufacturing Capacity, 2021 | Wind (Onshore) | Wind (Offshore) | Solar PV |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 59% | 70% | 85% |
| Europe | 16% | 26% | 2% |
| North America | 10% | 0% | 1% |
| Asia Pacific | 9% | 4% | 11% |
| Central & South America | 5% | 0% | 0% |
| Africa | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Eurasia | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Middle East | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Global manufacturing capacity share is calculated by averaging the global manufacturing shares of individual components (i.e., wind: tower, nacelle, blade; solar: wafers, cells, modules). Percentages may not add up to 100 due to rounding.
According to research by ONYX Insight, almost 60% of wind farm operators reported that supply chain issues were their biggest challenge over the next 2–3 years.
International collaboration and investment, however, can help diversify manufacturing outside of China. In addition, policymakers can also implement policies and incentives that encourage the growth of local manufacturing capacity for renewables.
All in all, streamlining processes, investing in infrastructure, and promoting local manufacturing can pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Download the 2023 Decarbonization Report.
Clean Energy
Visualized: The Four Benefits of Small Modular Reactors
What advantages do small modular reactors offer compared to their traditional counterparts?
Visualized: The Four Benefits of Small Modular Reactors
Nuclear power has a crucial role to play on the path to net zero. Traditional nuclear plants, however, can be costly, resource-intensive, and take up to 12 years to come online.
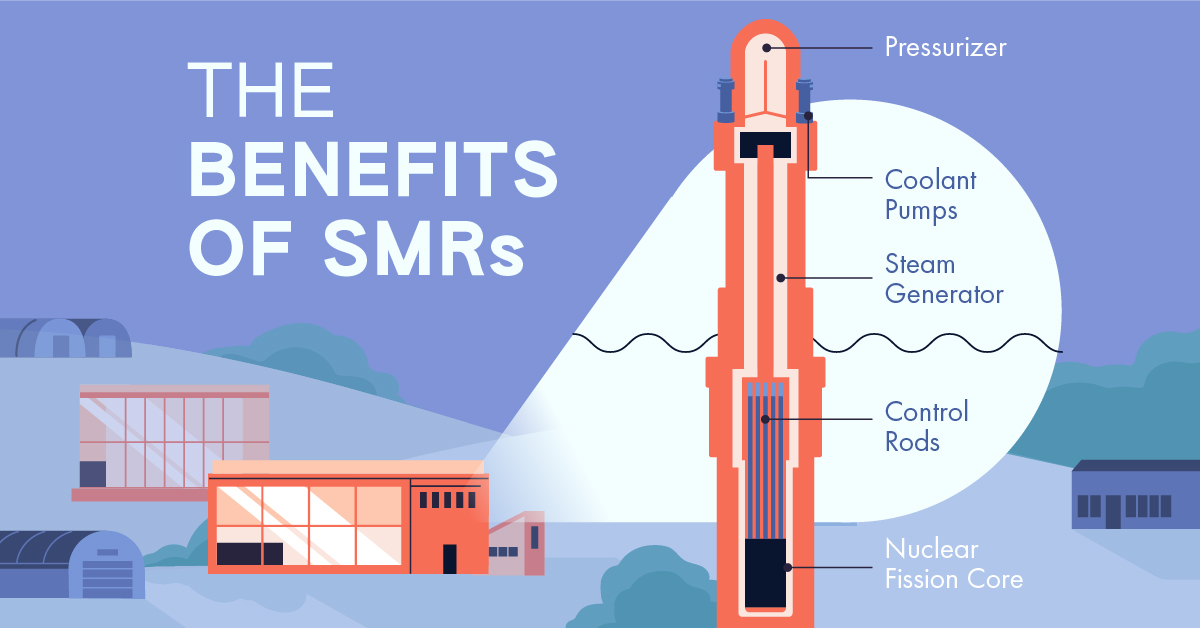
Small modular reactors (SMR) offer a possible solution.
Created in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, this infographic explores some of the benefits SMRs can offer their traditional counterparts. Let’s dive in.
The Four Key Benefits of SMRs, Explained
An SMR is a compact nuclear reactor that is typically less than 300 megawatts electric (MWe) in capacity and manufactured in modular units.
Here are some of the benefits they offer.
#1: Lower Costs
SMRs require a lower upfront capital investment due to their compact size.
SMRs can also match the per-unit electricity costs of traditional reactors due to various economic efficiencies related to their modular design, including design simplification, factory fabrication, and potential for regulatory harmonization.
#2: Quicker Deployment
Traditional nuclear plants can take up to 12 years to become operational. This is primarily due to their site-specific designs and substantial on-site labor involved in construction.
SMRs, on the other hand, are largely manufactured in factories and are location-independent, which minimizes on-site labor and expedites deployment timelines to as little as three years. This means they can be deployed relatively quickly to provide emissions-free electricity to the grid, supporting growing electricity needs.
#3: Siting Flexibility and Land Efficiency
SMRs have greater siting flexibility compared to traditional reactors due to their smaller size and modular design. In addition, they can utilize land more effectively than traditional reactors, yielding a higher output of electrical energy per unit of land area.
| Rolls-Royce SMR, UK (Proposed) | Median-Sized U.S. Nuclear Plant | |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | 470 MW | 1,000 MW |
| Area Requirement | 10 Acres* | 832 Acres |
| Land/Space Efficiency | 47 MW/Acre | 1.2 MW/Acre |
*Estimated area requirement
Given their flexibility, SMRs are also suitable for installation on decommissioned coal power plant sites, which can support the transition to clean electricity while utilizing existing transmission infrastructure.
#4: Safety
SMRs have simpler designs, use passive cooling systems, and require lower power and operating pressure, making them inherently safer to operate than traditional reactors.
They also have different refueling needs compared to traditional plants, needing refueling every 3–7 years instead of the 1–2 years typical for large plants. This minimizes the transportation and handling of nuclear fuel, mitigating the risk of accidents.
The Road Ahead
As of early 2024, only five SMRs are operating worldwide. But with several other projects under construction and nearly 20 more in advanced stages of development, SMRs hold promise for expanding global emission-free electricity capacity.
With that said, certain obstacles remain for the wide-scale adoption of SMRs in the United States, which was particularly apparent in the 2023 cancellation of the NuScale SMR project.
To fully realize the benefits of SMRs and advance decarbonization efforts, a focus on financial viability, market readiness, and broader utility and public support may be essential.
Learn how the National Public Utilities Council is working toward the future of sustainable electricity.
Clean Energy
The $3 Trillion Clean Energy Investment Gap, Visualized
In this graphic, we explore the $3 trillion clean energy investment gap visualized by sector, according to BloombergNEF data.
The $3 Trillion Clean Energy Investment Gap, Visualized
Global investment in the clean energy transition grew by 17% in 2023, showing resilience despite geopolitical tensions, high interest rates, and inflation.
But was it enough to keep the world on track to hit net zero by 2050?
To answer this question, we compare 2023 clean energy investment by sector with what’s annually needed to reach net zero by 2050, in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council.
The Investment Gap, By Sector
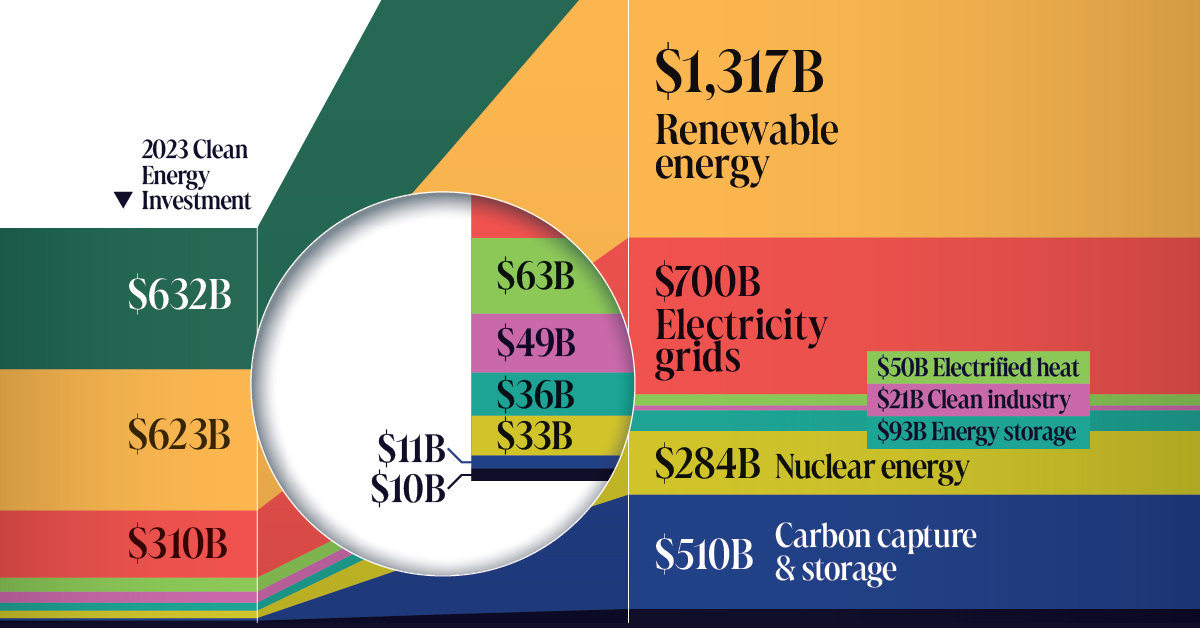
According to BloombergNEF data, annual global investment in the energy transition is at an all-time high. Despite this, only the electrified heat and clean industry sectors are meeting the thresholds necessary to hit net zero by 2050.
| 2023 Investment | Required Annual Investment for Net Zero*, 2024–2030 | Investment Gap | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrified transport | $632B | $1,805B | $1,173B |
| Renewable energy | $623B | $1,317B | $694B |
| Electricity grids | $310B | $700B | $390B |
| Electrified heat | $63B | $50B | -$13B |
| Clean industry | $49B | $21B | -$28B |
| Energy storage | $36B | $93B | $57B |
| Nuclear energy | $33B | $284B | $251B |
| Carbon capture and storage (CCS) | $11B | $510B | $499B |
| Hydrogen | $10B | $62B | $52B |
| TOTAL | $1,767B | $4,842B | $3,075B |
*BloombergNEF’s Net-Zero 2050 Scenario
To stay on track for net zero by 2050, the yearly investments in electrified transport, renewable energy, power grids, and energy storage must more than double their current rates for the rest of the decade.
Hydrogen, nuclear, and carbon capture and storage (CCS) have an even steeper hill to climb and must grow 6, 9, and 46 fold, respectively.
The Path Forward
It’s important to note that despite the current annual investment gap of $3T, the clean energy industry continues to exhibit positive trends.
Investment in electrified transport, for instance, surpassed that in renewable energy for the first time in 2023, marking a win for the sector.
Emerging sectors also experienced robust expansion despite being furthest off-target. Investments in hydrogen tripled to $10B, CCS nearly doubled to $11B, and energy storage witnessed a 76% increase to reach $36B in 2023.
These encouraging developments underscore the industry’s potential to drive transformative change and pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape in the years ahead.
Learn how the National Public Utilities Council is working toward the future of sustainable electricity.
-
 Electrification1 year ago
Electrification1 year agoVisualized: How the Power Grid Works
-
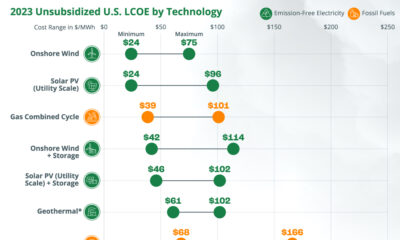
 Energy Shift9 months ago
Energy Shift9 months agoRanked: The Cheapest Sources of Electricity in the U.S.
-
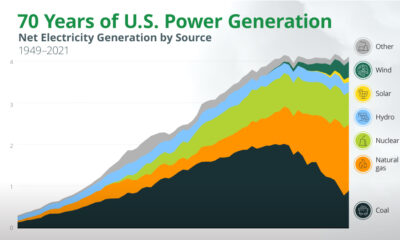
 Energy Shift1 year ago
Energy Shift1 year agoAnimated: 70 Years of U.S. Electricity Generation by Source
-
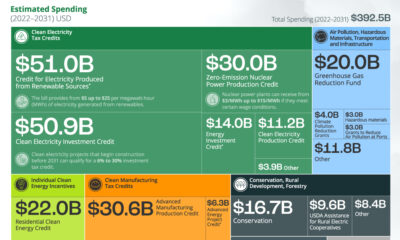
 Clean Energy1 year ago
Clean Energy1 year agoBreaking Down Clean Energy Funding in the Inflation Reduction Act
-
 Emissions1 year ago
Emissions1 year agoVisualizing Global Per Capita CO2 Emissions
-
 Decarbonization1 year ago
Decarbonization1 year agoThe U.S. Utilities Decarbonization Index
-
 Clean Energy1 year ago
Clean Energy1 year agoThe 30 Largest U.S. Hydropower Plants
-

 Clean Energy7 months ago
Clean Energy7 months agoBreaking Down the $110 Trillion Cost of the Clean Energy Transition

